Fully Validated Metabolite Quantification in Urine Using NMR
Complete the form below to unlock access to ALL audio articles.
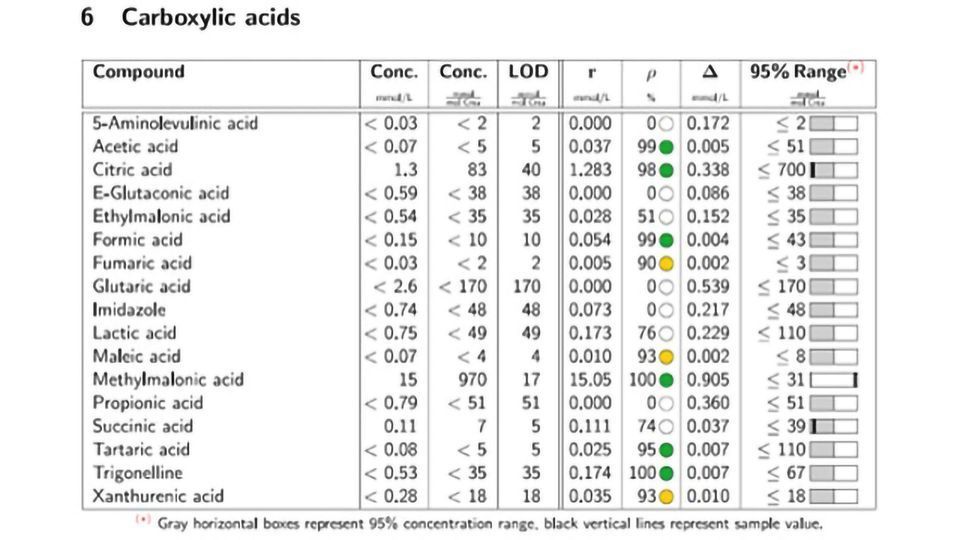
Bruker has announced the release of the B.I.QUANT-UR™ 1.1 module, an analysis solution that complies with DIN-ISO criteria for the identification and quantification of urine metabolites on Bruker’s nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in-vitro diagnostic research (Avance™ IVDr) platforms. The module automatically quantifies up to 150 endogenous and disease-related metabolites from urine, allowing users to obtain precise, sensitive and fully reproducible results, even below the limit of detection (LOD).
NMR produces highly reliable quantification values from a single experiment, which would traditionally require multiple tests with different sample preparations using techniques such as conventional gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or ion exchange chromatography mass spectrometry (IEC-MS). B.I.QUANT-UR 1.1 combines the raw concentration of a compound with quality assessment parameters to obtain reliable quantification results, which has potential in clinical and translational research. The new module introduces two additional parameters to provide confidence in quantification: signal correlation (ρ,%) to characterize the match between the lineshape metabolite signal and the calculated fit, with color coded flags added for improved visualization; and concentration error (Δ,mmol/L), for the concentration equivalent of the difference between metabolite signal and the calculated fit.
A key challenge in quantifying metabolites in urine is the complexity of the sample, which contains thousands of compounds generating multiple NMR signals. A unique feature of B.I.QUANT-UR includes DIN-ISO conformant wet spiking, to identify correct signals where there is significant overlap. This upgraded version of the successful B.I.QUANT-UR 1.0 module represents another iteration of a unique feature known as numerical spiking, where pure compound spectra of all 150 metabolites are automatically added to more than 20,000 urine spectra, and subjected to the quantification algorithm to determine the respective probabilistic LOD.

