Decoding Ambiguity: Context is crucial
Complete the form below to unlock access to ALL audio articles.
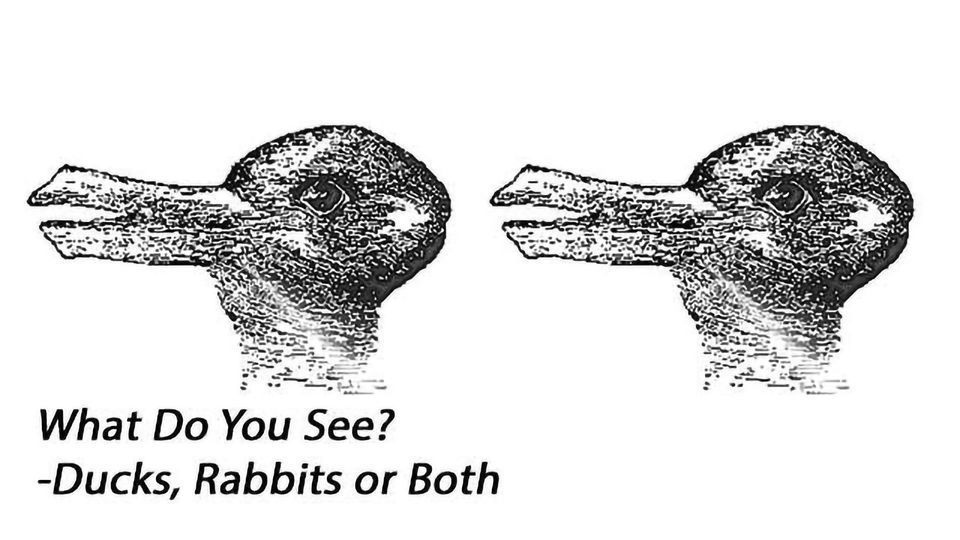
When you look at the two images above, what do you see? Maybe you see two ducks, sitting side by side. Perhaps instead you see two rabbits. Maybe you see a duck and a rabbit.
Now look at the image, and imagine a duck eating a rabbit. Can you see it now?
You’re not the only one who needs prompting to see both images side by side, according to research from University of Alberta neuroscientist Kyle Mathewson. About half of people can’t see both a duck and a rabbit at first glance. The flip takes place only when you ask them to imagine a duck eating a rabbit.
“Your brain sort of zooms out and can see the big picture when the images are put into context with one another,” said Mathewson, an assistant professor in the Department of Psychology.
Context is crucial
The study shows that a short cue—like “duck eats rabbit”—can give our brain the context it needs to distinguish between two identical images.
“This study also demonstrates that we can control the brain’s way of interpreting information with just a few words or with an image,” explained Mathewson. “We should all be mindful of that when, for example, we’re reading a news story. We’re often interpreting and understanding information the way we want to see it.”
The study also aimed to determine whether another, more simple phrase would work—namely, “Imagine a duck beside a rabbit.” But this phrase did not have the same effect, because it does not explain which image should be a duck and which should be a rabbit.
“What we discovered is that you have to come up with a way to disambiguate the scene, to allow the brain to distinguish between two alternatives,” said Mathewson.
This article has been republished from materials provided by The University of Alberta. Note: material may have been edited for length and content. For further information, please contact the cited source.
Reference:
Mathewson, K. E. (2018). Duck Eats Rabbit: Exactly which type of relational phrase can disambiguate the perception of identical side by side ambiguous figures? Perception

