New mouse brain map may illuminate origins of mental illnesses
Complete the form below to unlock access to ALL audio articles.
Scientists at Duke University have released a highly detailed model of connections in the mouse brain that could provide generations of neuroscientists new insights into brain circuits and origins of mental illness, such as depression and schizophrenia. The findings are published in the journal Cerebral Cortex.
Scientists conduct millions of experiments every year with mice, which have been genetically modified to mimic human disease. Having a far more precise model of the mouse brain will enhance knowledge about the connection between genetics and corresponding human disease, according to G. Allan Johnson, director of the Duke Center for In Vivo Microscopy.
"Interest in structural brain connectivity has grown with the understanding that abnormal neural connections play a significant role in neurologic and psychiatric diseases," Johnson said. "Examining brain connectivity in small animals can help us better identify problems in the diseased brain, and apply that knowledge to humans."
The scientists created the connectome, or map of brain circuitry, by performing an MRI scan of the brain of a healthy mouse at spatial resolution more than 100,000 times greater than that of a conventional clinical MRI. Data were acquired using diffusion MRI, which traces the pathways of nerve fibers called axons throughout the brain.

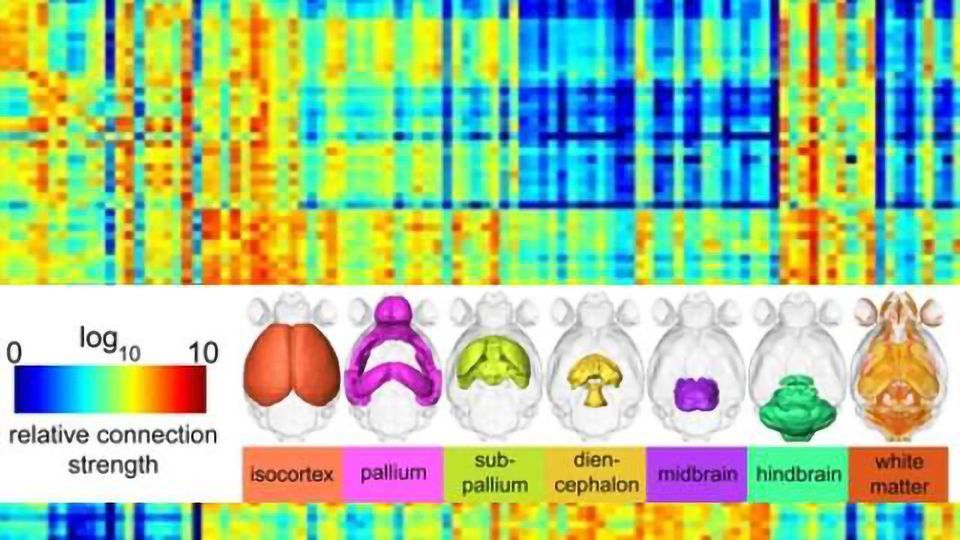
This matrix demonstrates the connectivity among different regions of the mouse brain. Relative connectivity estimates between 148 anatomic regions are displayed with a log10 scale color map (top left). Tractography seeds (rows) and targets (columns) are organized based on their developmental origins as indicated by colored surface renderings of parent structures along the top and left side of the figure. Credit: Duke Medicine
The accuracy of the connectome is determined by the spatial resolution and the number of different angles scanned. These new data are more than 1,000 times more precise than previous diffusion MRI scans of the mouse brain, Johnson said.
"Prior approaches to provide maps of the mouse brain have relied on fluorescent dyes injected into the brain," Johnson said. "The brain is then cut in thin slices, digitized and put back together again in a computer. It's pretty tedious."
Producing these high-resolution MRI images also has its challenges, he said. Scanning even a tiny mouse brain at such close detail creates a daunting amount of data that has in the past made such a project impractical, Johnson said.
But banks of high-powered computers have now allowed the scientists to capture and house the data and mathematically manipulate them to create the large 3-dimensional, digital models.
The colorful connectivity matrix charts each region of the mouse brain and its probable connectivity to other brain structures.The researchers are currently building an online portal for scientists around the world to access the full directory of digital files to guide their own research into mouse neurocircuitry.
Note: Material may have been edited for length and content. For further information, please contact the cited source.
Duke University School of Medicine press release
Publication
Johnson GA et al. A Diffusion MRI Tractography Connectome of the Mouse Brain and Comparison with Neuronal Tracer Data. Cerebral Cortex, Published Online June 5 2015. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv121

